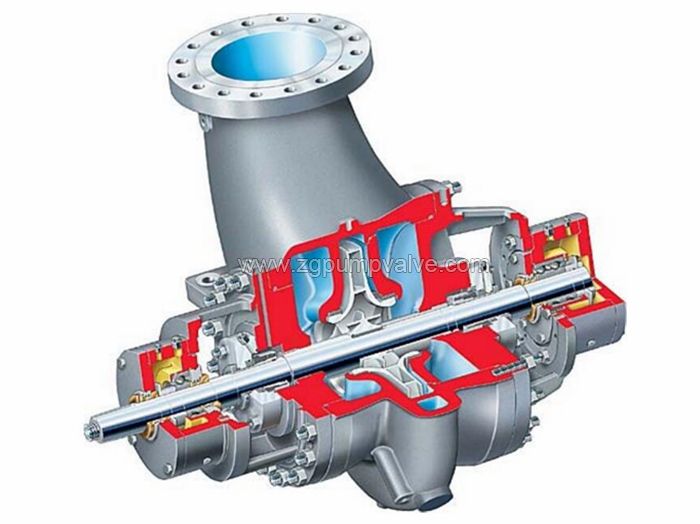
Chemical Pump
CHEMICAL PUMP
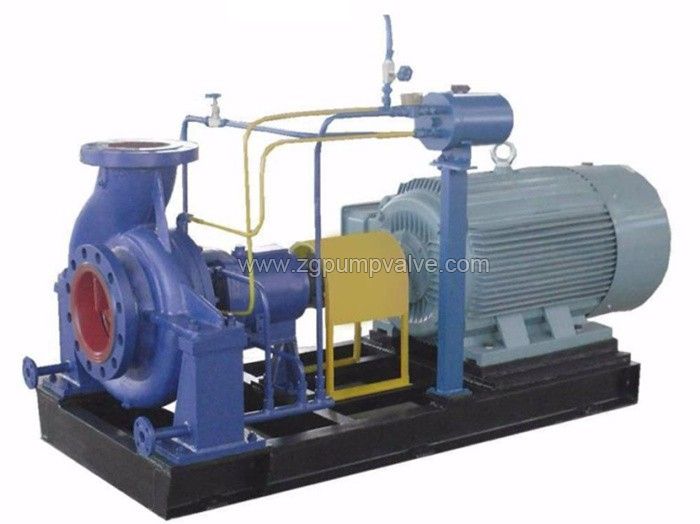
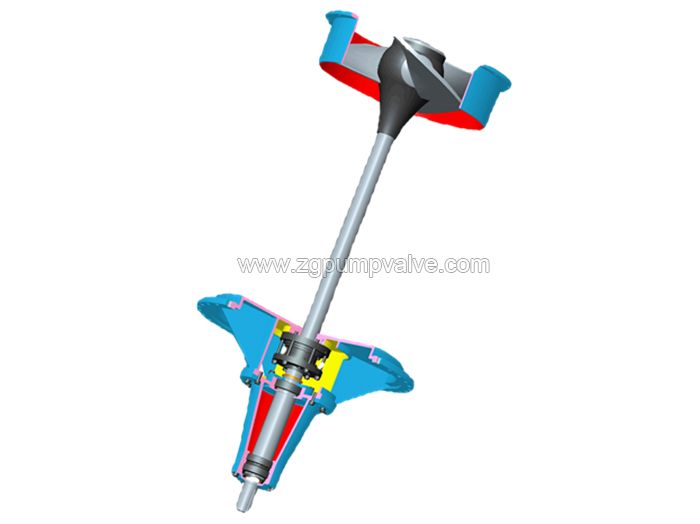
Chemical pumps are the essential dynamic equipment of the chemical factories, among which the most used is the horizontal chemical process pump. Horizontal axial flow pumps are used for forced circulation of the evaporation process. Vertical mixed flow pumps and other vertical long shaft submerged pumps are used in different sump conditions.
Chemical pumps often operate in high temperature and high pressures circumstances, for conveying strong acids and alkalis, corrosive, flammable and explosive, abrasive solutions. High quality, excellent performance, reliable, low consumption chemical pumps should be supplied for chemical and petrochemical industry.
Advanced manufacturing methods and reliable material technology enable us to develop highly specialized and tailored pumping solutions for our customers.
Highly customized:
→ Meet particular working conditions: big diameter impellers and hydraulic design meet the flow rate and head.
→ Meet extreme temperature: centerline support structure or bearing cooling device could be adopted
→ Meet abrasive solution containing particles: silicon carbide /SiC ceramics lining, wear-resistant cast iron, chromium alloy
Material:
A group of wear- and/or corrosion-resistant materials: Stainless steel, SS304, Duplex stainless steel, SS316, SS316L, 904L, Titanium, Titanium alloy, Nickel, Hastelloy, Monel. Chemical Pumps are made of these special materials perform well even under the most severe service conditions.
1. What is a Chemical Pump?
Chemical pumps are particularly designed and built to manage the transportation of various corrosive chemical solutions or other hazardous materials at ambient or high temperatures; thus, the chemical pumps must be corrosion resistant, high temperature resistant and sometimes abrasion resistant. Those pumps are widely used in industries including chemicals, petrochemicals, agrochemicals, water treatments, metallurgy, lithium battery...
2. How Does a Chemical Pump Work?
Chemical pumps operate by generating pressure to transfer the chemical solutions between locations. Different pump designs achieve this pressure in various ways, but most chemical pumps need the rotating impellers or rotors to produce the necessary force for fluid movement.
3. Various Types of Chemical Pumps
There are various chemical pumps available for different requirements, and according to their structures, materials and working principles, there are many types of them in the market, we’ll list some of the most widely used types of chemical pumps as below:
3.1 Centrifugal Chemical Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are widely used among different industries as the ideal choices for chemical solution pumping. They convert rotational energy into kinetic energy through an impeller or several impellers, and the kinetic energy is gathered by the pump casing, finally the fluid with kinetic energy will be pushing towards the discharge outlet. These chemical centrifugal pumps are renowned for their reliability, efficiency and affordability, and are suitable for handling low-viscosity mediums with minimal solid content.
3.2 Chemical Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that moves chemical fluids using a flexible diaphragm. They generate suction by shifting the diaphragm back and forth, pulling liquid into the chamber and then push it out. These chemical diaphragm pumps are suitable for corrosive, thick or abrasive fluids and they are perfect for situations where a smooth, low-shear pumping action is needed.
3.3 Chemical Peristaltic Pumps
Peristaltic pumps work like a mechanical version of swallowing - rollers squeeze a flexible tube to create a vacuum that pulls fluid in and pushes it forward. These chemical peristaltic pumps are quite suitable when you're dealing with high density and abrasive liquids or need precise dosing, since the fluid only contacts the replaceable tube, making them easy to maintain.
3.4 Chemical Piston Pumps
The working principle of a piston pump is similar to that of a precision syringe – its reciprocating motion generates suction, thereby drawing in the liquid, and then expelling it under pressure. What makes these chemical piston pumps special? They are capable of handling challenging tasks: they can push thick, coarse liquids, or provide a stable flow in high-pressure systems, while other pumps would struggle in such situations.
3.5 Magnetic Drive Chemical Pumps
The magnetic drive pump (magnetic pump) uses a magnetic coupling system to achieve liquid transportation, while ensuring complete isolation between the motor and the pump components. This design utilizes the electromagnetic field to drive the impeller to rotate, thereby enabling the liquid to flow within the system. The sealing characteristics of these pumps make those chemical magnetic drive chemical pumps particularly suitable for handling corrosive chemicals and applications where strict leakage prevention is required.
3.6 Chemical Gear Pumps
The working principle of a chemical gear pump is to achieve positive displacement through the coordinated rotation of two precisely meshing gears. As the gears rotate, the chemical fluid is trapped in the gap between the gear teeth and the pump casing, and then is pushed towards the outlet. This design performs particularly well in handling chemical fluids with high viscosity, and also offers excellent performance in high-capacity transportation applications.
3.7 Chemical Progressive Cavity Pumps
The progressive cavity pump (commonly referred to as a screw rotor pump or eccentric screw pump) achieves liquid transportation by having a precisely designed screw rotor rotate within an elastic stator. The progressive cavities formed between the rotor and the stator create independent sealed chambers, which continuously advance from the suction end to the discharge end. This unique working principle makes the progressive cavity chemical pumps particularly suitable for handling viscous, shear-sensitive, or abrasive mediums, while also maintaining a stable flow rate and reducing pulsation.
3.8 Chemical Rotary Lobe Pumps
The rotary lobe pump transports fluids through the cavities formed between two rotating vanes and the pump casing, thereby gradually delivering the fluid to the pump discharge. The rotary lobe chemical pumps can effectively handle fluids of different viscosity ranges and maintains gentle product handling characteristics during the transportation process.
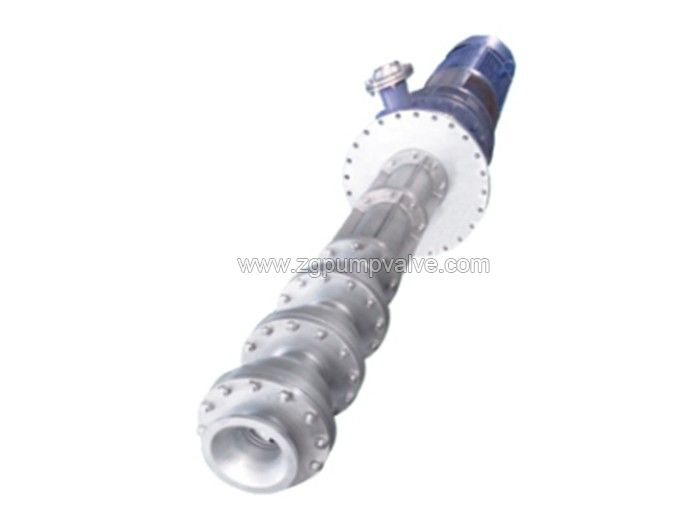
3.9 Chemical Submersible Pumps
The submersible pump is completely submerged in the liquid it is conveying during operation. These pumps come in various configurations such as centrifugal, diaphragm, and piston types, and can meet various operational requirements. The submersible chemical pumps are particularly suitable for liquid transportation from oil wells, collection tanks, and storage tanks.
4. How to Selecting the Right Chemical Pumps?
Selecting the appropriate chemical pumps requires comprehensive consideration of multiple parameters, including fluid characteristics, required flow rate, working pressure requirements, and installation conditions, etc. When selecting a chemical pump, please refer to the following suggestions:
4.1 Figure out the fluid characteristics: The properties of the fluid, such as viscosity, chemical corrosiveness and thermal characteristics, will directly affect the applicability of the chemical pumps. When making a selection, these parameters must be taken into account to ensure that the selected materials and design are compatible with the process medium.
4.2 Figure out the required flow rate: Flow capacity refers to the volume of fluid that passes through in a unit of time, usually in cubic meter per hour and liter per second. Please select the chemical pump that meets the flow requirements specified by your system.
4.3 Figure out the required pump head: The system pressure requirements determine the required pump head. Please confirm that the required pump head of the selected centrifugal chemical pump to meet your application specifications.
4.4 Consider the site conditions: The site conditions of chemical pumps including the site altitude, temperature, humidity, rain conditions, earthquake records, presence of hazardous gas or dusts...all of them can affect the model selections of chemical pumps. The selected pumps must be able to work safely in the site environment.
4.5. Selection of pump materials: The wetted parts material of chemical pumps is supposed to be corrosion resistant to the pumping fluids and compatible to the site environment, otherwise the pumps would fail shortly and even pollute the environment.
4.6. Determine the pump type: It is important to have clear understanding of what type of chemical pump is suitable to your applications, as different pumps have their own features, choosing the right pump requires some basic knowledges of chemical pumps, please feel free to contact us if you need any assistance in this regard.
5. Where the Chemical Pumps Can be Used?
Chemical pumps are widely required in different industries due to their features of corrosion resistant, high temperature resistant, below are some typical applications for those chemical pumps:
5.1 Chemical plants
In chemical manufacturing plants, specialized chemical pumps play a crucial role in transporting various liquids within production process. These industrial chemical pumps are specifically designed to safely handle corrosive materials, including strong acids, alkaline solutions, and industrial solvents.
5.2 Petrochemical plants:
The oil and gas sector relies on the technology of chemical pumps to transfer various process chemicals, from drilling fluids to corrosive acids and bases, during well drilling and hydrocarbon extraction.
5.3 Water treatment plants
In potable water treatment plants, these corrosion-resistant chemical pumps handle aggressive water treatment chemicals, from chlorine-based disinfectants to alkaline neutralizers and acidic cleaners.
5.4 Pharmaceutical plants
In the process of drug formulation and production, chemical pumps facilitate the controlled transmission of various fluid types, including purified solvents, mechanical lubricants, and active pharmaceutical ingredients in solutions.
5.5 Agriculture and Agrochemical plants
The chemical pumps are widely used in both agriculture and agrochemical plants for handle corrosive chemical solutions of raw materials of fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides.
5.6 Mining Industries
Mining operations routinely need corrosion-resistant centrifugal chemical pumps to handle aggressive chemicals like sulfuric acid throughout mineral extraction and processing.
6. Maintenance Instructions of Chemical Pumps
The reliability of chemical pumps relies on proper maintenance procedures. The maintenance team should regularly inspect the quick wear parts (such as mechanical seals, impellers, and rotating shaft). Sticking to the operating and cleaning standards recommended by the chemical pump manufacturer is crucial for the continuous operation and longevity of the equipment. One important notice: using the original pump parts from the pump manufacturer is essential for the maintenance.
7. Advantages of Chemical Pumps
7.1 Corrosion & High temperature resistant
The unique design of this chemical resistant pump enables it to reliably handle dangerous chemical liquids that would quickly damage ordinary water pumps. Whether it is transporting boiling caustic soda or high temperature acid fluids, these specialized chemical pumps can prevent leaks and malfunctions, thereby avoiding the endangerment of workers or facilities - this is a crucial safety feature for chemical operations.
7.2. Operational Cost Low
These specialized chemical pumps are specially designed to maintain durability in extreme chemical environments, thereby significantly reducing downtime, lowering the frequency of failures and replacements. The reduced maintenance requirements directly lead to cost savings and uninterrupted production - bringing a competitive advantage to the operation.
7.3 Efficiency Increasing
The optimized hydraulic design of the chemical pumps can maintain a stable volume output, thereby achieve a predictable chemical injection rate and avoid process fluctuations. Such a level of control is crucial for efficient operation, as it can eliminate inaccurate metering and reduce excessive consumption of chemical substances.
7.4 Multi-functional
Chemical pumps are available in diverse configurations - varying by design, capacity, and construction materials - to meet the specific demands of different processing applications. Their operational flexibility enables them to handle a wide range of substances, from dilute solvents to thick and viscous compounds, thus making them a universal solution applicable to various chemical industries.
7.5. Operation Safe
These specialized chemical pumps have been meticulously designed to resist the corrosion of powerful chemicals and meet strict safety standards. They can effectively isolate hazardous substances. This protective design concept significantly reduces the risks in the workplace and prevents pollution of the environment.
8. Disadvantages of Chemical Pumps
Chemical pumps have significant processing advantages, but they also present some operational challenges during operations. Before those chemical process pumps, it is necessary to first understand their potential limitations. In this paragraph, we will discuss this in detail.
8.1 Higher Initial Purchasing Cost
The main shortcoming of chemical pumps is their comparatively high initial cost. Compared with general standard water pumps, their specialized structure and materials result in significantly higher procurement costs, which is a crucial consideration for small and medium-sized enterprises with limited funds.
8.2 Higher Maintenance Costs
The chemical pumps are with robust design and fine quality, but they still need in time maintenances to ensure the smooth operation. However, the spare parts of those chemical pumps are relatively higher in cost due to their design as well as material of construction.
8.3 Limited Compatibility
Not all chemical pumps can handle every type of chemical solution. Their materials and designs must be compatible with the specific chemical solution they are dealing with. Incompatible pump configuration can lead to catastrophic failures, endangering the integrity of personnel, equipment, and the surrounding ecosystem.
8.4 Dimension Restrictions
Due to the robust design of chemical pumps, they generally have relatively bigger sizes than regular water pump. This disadvantage must be well considered during the design of the pumping system, otherwise there would be problems for the installation of pumps.
8.5 Operational Difficulty
Due to the multi-functional design of centrifugal chemical pumps, it requires the operating workers to have more professional knowledges regarding the working principle of those pumps. The wrong operation would cause malfunction of pumps, or even cause severe injury to personnels.
9. Operational Safety Precautions of Chemical Pumps
During the operation and maintenance of chemical pumps, the necessary safety precautions as below must be taken to avoid accidents and physical injuries:
9.1 Proper Training
Do not operate the chemical pump without proper training - understanding its design, components and usage limitations is crucial. You should also be clear about which chemicals the pump can handle and how to deal with it in case of failure. Skipping this step may result in equipment damage, dangerous leaks and even more serious consequences.
9.2 Protections
Working with chemical pumps should never skip personal protective equipment (PPE)—chemical-resistant gloves, sealed goggles, and full-body coverage are necessities. That equipment is the only thing standing between workers and corrosive splashes, toxic absorption, or worse when seals failure or lines rupture.
9.3 Well Ventilation Conditions
Do not operate chemical pumps in enclosed spaces - good ventilation is crucial for discharging toxic gases and preventing the accumulation of explosive gases. An exhaust system should be installed, air quality should be monitored, and unobstructed airflow should be maintained. Otherwise, workers may be exposed to harmful gases and a flash fire may occur.
9.4 In-time Inspection & Proper Maintenance
The in-time inspection and proper maintenance of chemical pumps is the precondition of the smooth operation of those pumping equipment, the recommended interval of inspections is every two weeks, and the inspection should at least include the checking for leaks, vibrations, bearing temperatures, noise as well as flow rate & head...The potential issues must be found from the inspections to avoid any damages.
9.5 Compatibility of Pumps & Fluids
Making sure that the pumping fluids are compatible with the pump’s wetted parts material, otherwise the pump could be damaged in a short period of time due to the corrosion or high temperature, and therefore cause tremendous loss. It is important to stick to the original purpose of the chemical pumps or follow the instructions from your pump suppliers.
9.6 Emergency Procedures
The emergency procedures are the quite important, as they can reduce the loss a lot once the accidents happen, strictly follow those procedures will be the last measure to avoid the expansion of loss. Thus, the workers must receive proper training regarding to the emergency procedures of operation of chemical pumps.
10. Summary & Final Thoughts
Chemical pumps are indispensable pumping equipment in the industrial sector. They can precisely and efficiently convey various liquids and chemical solutions of different temperatures and corrosive properties. There are multiple variants of such chemical pumps, each with its own unique operating characteristics and limitations. To achieve optimal performance and extend service life, it is essential to strictly follow maintenance procedures, adopt appropriate operating protocols, and implement comprehensive safety measures.
Read More